Marketing Management Cycle
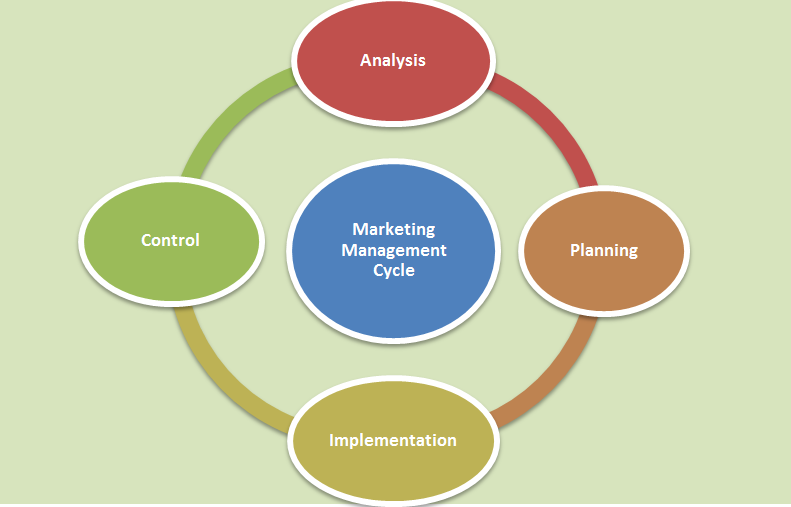
The marketing management cycle is based on four main activities that guide the process of analyzing, planning, implementing, and controlling marketing strategies. These activities are:
A. Strategic Analysis
Strategic analysis is the first activity, which involves gathering and analyzing information in order to make investment decisions and develop functional area strategies. To determine the company’s competitive advantage, market research is conducted to identify customer needs and preferences, and competition is analyzed to identify opportunities and threats.
An important outcome of the strategic analysis phase is the identification of target markets. Marketers can identify segments of the market most likely to be interested in their products or services by analyzing customer preferences and needs. Marketing strategies based on this information can then be designed to meet the specific needs of these segments.
Investment decisions and strategies for functional areas are influenced by strategic analysis. Here’s how:
i. Contribute to the Investment Decisions
Marketers gather and analyze information about market trends, customer needs and preferences, and competitive landscapes during strategic analysis to contribute to investment decisions. Marketing strategies are then evaluated in terms of feasibility and potential success based on this information. A marketer can use this analysis to determine which marketing initiatives to pursue and how much to invest in each one.
For example, marketers may recommend investing more resources in a marketing channel if the analysis reveals that the channel is highly effective in reaching the target audience.
ii. Selection of Functional Area Strategy
Strategic analysis is also useful for selecting functional area strategies. Different departments within an organization are known as functional areas, such as product development, pricing, distribution, and promotion. It is essential for developing effective strategies in these functional areas to develop insights into customer preferences, market trends, and competitive landscape through strategic analysis.
Based on the analysis, marketers may suggest that a new product be developed that addresses a specific customer need. They may also suggest pricing strategies that are competitive and appealing to target audiences. It is possible for marketers to recommend a channel that is most effective in reaching the target audience based on an analysis of distribution channels.
B. Marketing Planning
In the marketing management cycle, marketing planning entails four major activities that are crucial to its success. Let’s discuss each of these in detail.
i) Determining Business Missions and Goals
To begin, determining a company’s mission and goals is essential to marketing planning. The mission statement describes a company’s overall purpose, the products, and services it offers, as well as the market it serves. The purpose and objectives of the organization must be defined.
In order to ensure that goals are meaningful and achievable, they must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
ii) Developing Strategic Alternatives
Next, the business must develop strategic alternatives once it has established its mission and goals. A strategic alternative is a course of action that the organization can take to achieve its goals. It involves identifying several options the organization can pursue to achieve its goals.
When developing strategic alternatives, marketing managers must take factors such as customer needs, market trends, competitive pressures, and technological advancements into account.
iii) Specifying Operational Tasks
When the strategic alternatives have been identified, the next step is to specify the operational tasks necessary for implementing the selected strategy. This involves identifying the specific actions that the organization must take to reach its goals. Operational tasks may include the development of new products, pricing strategies, promotion tactics, and distribution channels.
iv) Designing Contingency Strategies
A final step in marketing planning is developing contingency strategies. These are backup plans in case the primary strategy does not perform as expected. In the event of unexpected changes in the market environment, contingency strategies help the organization respond quickly and effectively.
In conclusion, marketing planning is a vital component of the marketing management cycle since it helps the organization identify and define operational tasks, as well as design contingency strategies to accomplish its goals.
C. Implementation
Within the marketing management cycle, implementation is the third major activity. In this activity, each marketing unit and personnel are assigned tasks, targets, authority, and responsibilities to implement the marketing plan. There are several crucial steps involved, including:
i. Assigning tasks, targets, authority and responsibilities to each marketing unit and personnel:
It includes dividing the marketing plan into smaller tasks and assigning them to specific marketing units or personnel who will be responsible for executing them.
The marketing team must define the overall marketing objectives and goals of the company, identify the tasks and activities required to achieve these objectives and assign specific tasks and responsibilities to each marketing unit and personnel in accordance with their skills, expertise, and experience.
A common goal must be established for each marketing unit and personnel, as well as the necessary authority for each team member to accomplish his or her tasks efficiently.
ii. Preparation of Organizational Structure, Job Assignments, and Territory Allocation:
In order to effectively implement the marketing plan, the marketing team needs to determine the appropriate organization structure, job assignments, and territory allocation.
An organization structure identifies the number of employees needed, their job titles, and the reporting hierarchy, which ensures clarity on each employee’s role and responsibilities. Employees are then assigned jobs based on their skills and expertise. This helps to ensure that the best personnel are assigned to the jobs, thus increasing efficiency and productivity.
A company’s territory allocation involves determining which geographical areas each employee or team is responsible for. When assigning territories, it ensures that there are no overlaps or confusions when it comes to customer engagement, especially for companies with multiple locations or a large customer base.
This step is crucial to ensuring that the marketing team is organized and structured in a way that maximizes its efficiency and effectiveness.
iii. Establishing Internal Relationships of the Marketing Department with Various Departments:
The marketing team will need to establish relationships with various departments within the organization at this stage. It is possible to ensure that everyone works towards the same goal and that the marketing plan is executed smoothly by effective communication and collaboration between different departments.
For the marketing strategy to align with the company’s goals, marketing teams need to work closely with other departments such as sales, product development, finance, and customer service. When it comes to generating leads and converting them into customers, the marketing team needs to work with the sales department.
Collaboration between departments can prevent conflicts and delays in implementing the marketing plan, as well as identify potential problems early on, allowing them to be resolved before they become more serious.
Ultimately, marketing teams need to establish strong relationships within their organizations in order to implement their marketing plans and achieve their goals.
iv. Designing Effective Coordination and Cooperation
In this step, the marketing team needs to establish effective coordination and cooperation with external agencies such as suppliers, transport companies, market research agencies, and advertising agencies. Having these agencies on board is important because they are crucial to a successful marketing campaign.
It is important for businesses to work closely with suppliers as they provide them with raw materials and finished goods for manufacturing their products, for example. It is possible to ensure that the marketing plan runs smoothly and the products are delivered to the customers on time if suppliers are coordinated effectively.
It is also important to coordinate with transport companies to ensure that the products are delivered on time and in good condition. In order for businesses to make informed decisions, having an effective relationship with market research agencies can help them understand the needs and preferences of their customers.
As an important partner, advertising agencies assist in the development and execution of effective advertising campaigns that can increase brand awareness and generate leads. In order to create targeted and effective campaigns that resonate with their target audience, businesses can coordinate with advertising agencies effectively.
To achieve their marketing goals, the marketing team must coordinate and cooperate efficiently with outside agencies.
v. Maintaining long-term relationships with customers and other key stakeholders and projecting a favorable public image about the company:
Customers and other key stakeholders such as suppliers, distributors, and investors must be the focus of the marketing team as they build long-term relationships. In order to achieve this, you must create a positive brand image, provide high-quality products and services, provide excellent customer service, and engage with your customers using various channels, such as social media and email marketing.
Customer feedback, complaints, and concerns must also be monitored and responded to in order to maintain customer loyalty and satisfaction. Public relations and corporate social responsibility activities can help to project a positive image.
Creating a clear chain of command and setting clear expectations and targets for each marketing unit and employee is essential to the successful implementation of a marketing plan. In order to ensure the marketing plan is executed effectively, and necessary adjustments are made to achieve the company’s goals, regular monitoring and evaluation of its progress are also essential.
Implementation is a critical phase that requires careful planning and coordination to ensure that the marketing plan is executed effectively, and the company’s objectives are met.
D. Control
In the marketing management cycle, control involves monitoring and evaluating the performance of the marketing plan to make sure it is meeting its objectives. Three types of control are used in this phase: annual plan control, efficiency control, and strategic control.
i. Annual Plan Control
It involves comparing actual performance to the company’s annual plan targets. This includes an analysis of the company’s financial performance in terms of sales, profits, and market share. In order to return the performance to its original level, this type of control identifies deviations from the planned targets and takes corrective actions.
As an example, if the company planned to sell a specific product at a certain level during a given period of time, it may compare the actual sales achieved to its target sales. Management may have to adjust the marketing strategy, reduce the price, increase promotional efforts, or modify the product features if the actual sales are below the planned target.
A company’s annual plan control program ensures that its marketing goals are being achieved by monitoring key performance indicators such as sales, market share, profits, and costs. By doing so, the management can identify any areas that aren’t performing as expected and take corrective measures.
ii. Efficiency Control
The effectiveness of marketing units, tasks, and personnel is the basis of efficiency control. The goal of Efficiency Control is to identify key performance indicators (KPIs) for each marketing task and monitor them regularly. Lead generation, customer acquisition, customer retention, and marketing campaigns can all be measured with KPIs.
Management can use Efficiency Control to identify areas where marketing activities aren’t performing well and take corrective measures to improve them. Management may need to adjust a marketing campaign’s strategy, target a different audience or allocate more resources if a marketing campaign doesn’t generate enough leads.
To ensure that the marketing personnel are contributing to the company’s overall marketing goals, Efficiency Control measures their productivity and effectiveness as well. Performance metrics such as sales targets, customer satisfaction ratings, and marketing campaign success rates can be tracked to achieve this.
In order to improve the efficiency of the marketing team, the management can monitor personnel performance and identify areas for additional training.
In summary, Efficiency Control ensures that marketing activities are performed efficiently and effectively, and that they contribute to the overall marketing goals of the organization.
iii. Strategic Control
As part of the marketing management cycle, strategic control ensures that the overall marketing goals, including customer satisfaction, are achieved. As part of this control method, the company evaluates the effectiveness of its marketing strategies and adjusts them as necessary to improve overall marketing performance.
The evaluation of a company’s performance in terms of meeting the marketing goal of customer satisfaction is a key component of Strategic Control. In order to assess how well the company meets the needs of its customers, the marketing management team may use a variety of metrics, like customer feedback surveys.
As a result of analyzing this data, a company can identify areas where it is failing and make necessary adjustments to improve customer satisfaction.
It is also important to evaluate the company’s overall marketing performance, including increasing market share, profitability, and sales, as part of Strategic Control. Key performance indicators are analyzed and compared to the Marketing Plan goals. In order to get the company back on track, the marketing management team must determine the reasons for not meeting the company’s goals and take corrective action.
Furthermore, Strategic Control involves monitoring external factors that may affect the success of marketing strategies, such as market changes and competitive pressures. In order to maintain its competitive edge, the company needs to stay aware of these changes and adjust its marketing strategies accordingly.
Ultimately, the marketing management cycle is a continuous process, and each activity is integral to long-term success for businesses. Businesses can achieve their strategic goals and deliver value to their customers by following this cycle.
- Firms Responses to Marketing Challenges – 11 Major Solutions for Overcoming Challenges | Principles of Marketing
- Marketing Challenges in the New Millennium – From Consumers’ and Marketing Firms’ Perspective | Principles of Marketing
- Project Management Life Cycle – Phases, Importance, Challenges | Project Management
- Phases of System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) – 9 Major Phases in SDLC | Management Information System